When evaluating Lonitab is a brand-name topical solution that delivers 5% minoxidil to the scalp for androgenetic alopecia, most people wonder how it stacks up against the myriad of other options on the market. You might be on a tight budget, worried about side effects, or simply confused by the flood of product names. This guide cuts through the noise, laying out clear criteria, side‑by‑side data, and real‑world pros and cons so you can pick the treatment that actually fits your needs.
Key Takeaways
- Lonitab uses the same active ingredient as generic minoxidil but is marketed with a unique delivery system.
- Oral finasteride targets the hormonal cause of hair loss, while topical minoxidil works by widening blood vessels.
- Non‑pharmacologic options like Nioxin focus on scalp health rather than hair‑follicle stimulation.
- Hair transplantation offers a permanent solution but comes with higher upfront cost and surgical risk.
- Choosing the right product depends on your hair‑loss stage, tolerance for medication, and budget.
How We Compare Hair‑Loss Treatments
To keep the comparison fair, we use a set of six decision criteria that matter most to most users:
- Active ingredient and mechanism - What does the product actually do at a cellular level?
- Formulation and concentration - Is it a foam, liquid, pill, or surgical graft?
- Regulatory status - FDA‑approved, prescription‑only, or over‑the‑counter?
- Typical cost - Monthly outlay for average users in the United States.
- Side‑effect profile - Frequency and severity of unwanted reactions.
- Best‑fit patient profile - Who sees the most benefit (early‑stage loss, advanced thinning, etc.).
Side‑by‑Side Comparison Table
| Product | Active Ingredient | Formulation | Typical Concentration | FDA Status | Average Monthly Cost (USD) | Common Side Effects | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lonitab | Minoxidil | Topical solution | 5% | OTC (approved) | $30‑$45 | Scalp irritation, unwanted facial hair | Early‑to‑moderate male/female pattern loss |
| Rogaine (generic) | Minoxidil | Foam or liquid | 5% (men) / 2% (women) | OTC (approved) | $35‑$50 | Dryness, itching, rare dizziness | Similar to Lonitab but offers multiple delivery formats |
| Finasteride (Propecia) | Finasteride | Oral tablet | 1mg daily | Prescription | $15‑$30 | Sexual dysfunction, decreased libido | Men with progressive androgenetic alopecia |
| Nioxin System 2 | Scalp‑care blend (niacin, antioxidants) | Shampoo, conditioner, scalp treatment | Varies per product | OTC (cosmetic) | $40‑$70 | Minimal; occasional scalp tightness | Those preferring non‑medicinal boost for thinning hair |
| Hair Transplant (FUT/FUE) | Autologous hair grafts | Surgical procedure | Permanent | Medical procedure (regulated) | $4,000‑$15,000 (one‑time) | Scarring, infection risk | Advanced loss, desire for permanent restoration |
Deep Dive Into Each Option
Rogaine is the most recognizable brand of minoxidil on the market. Launched in the 1980s, the product offers both a foam and a liquid version, letting users choose the feel they prefer. Clinical trials, such as the 2021 multicenter study funded by the FDA, showed an average 12% increase in hair count after 12months of twice‑daily use. The main advantage over Lonitab is the broader availability of concentration variants (2% for women, 5% for men) and a slightly larger body of long‑term data.
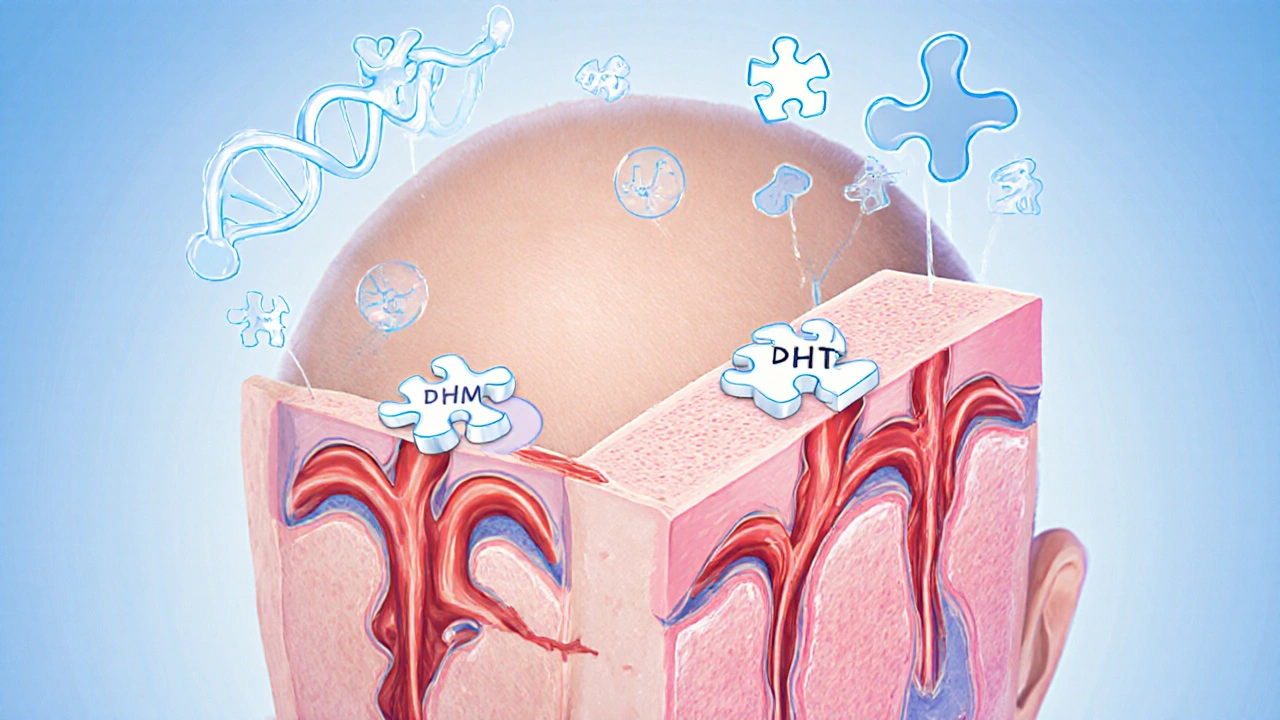
Finasteride, sold under names like Propecia, works by inhibiting the enzyme 5‑alpha‑reductase, which converts testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT). DHT is the primary hormone that shrinks hair follicles in androgenetic alopecia. By reducing scalp DHT levels, finasteride can halt progression and even regrow hair in many men. A 2022 meta‑analysis of 19 randomized trials reported a 66% success rate in preventing further loss, but sexual side effects remain a notable concern.
Nioxin is marketed as a scalp‑care system rather than a drug. Its proprietary blend includes niacin, antioxidants, and plant extracts that aim to improve blood flow and reduce oxidative stress. While not a direct follicle stimulant, many users notice a healthier looking hair shaft and less breakage. Because it’s classified as a cosmetic, it requires no prescription and carries virtually no systemic risk.
Hair transplant uses strip harvesting (FUT) or follicular unit extraction (FUE) to relocate healthy hair follicles from the back of the scalp to balding zones. Modern techniques can achieve graft survival rates above 95% when performed by experienced surgeons. The upside is a permanent solution with natural‑looking density, but the downside includes cost, recovery time, and the fact that it doesn’t stop future loss in untreated areas.
Pros and Cons of Lonitab
Let’s break down what makes Lonitab stand out and where it falls short compared to the alternatives.
- Pros
- Same proven active ingredient (minoxidil) with a proprietary solvent that claims better scalp absorption.
- OTC availability keeps the entry barrier low; no doctor visit needed.
- Cost‑effective per month compared with many premium brands.
- Suitable for both men and women when used twice daily.
- Cons
- Only offered in a 5% liquid; no lower‑strength option for women who may be sensitive.
- Potential for scalp irritation, especially if users apply on wet hair.
- Like all minoxidil products, results plateau after 6-12 months, requiring continued use.
- Does not address hormonal drivers of hair loss, so it may be less effective for those with high DHT levels.
Choosing the Right Treatment: A Simple Decision Guide
Answer the following three questions to narrow your options:
- Is your hair loss primarily due to hormonal DHT activity? If yes, consider adding an oral finasteride (or a topical DHT blocker) to your regimen.
- Do you prefer a non‑prescription, low‑risk approach? Then a minoxidil‑based product like Lonitab or Rogaine is a safe starting point.
- Are you looking for a permanent, high‑impact fix and willing to invest $5,000‑$15,000? A hair transplant performed by a board‑certified surgeon may be your best bet.
Most people find success with a combination: minoxidil for scalp stimulation plus finasteride for hormonal control. Always consult a dermatologist before mixing prescription and OTC products.
Safety, Side Effects, and What to Watch For
Minoxidil’s side‑effect profile is generally mild. The most common issues include:
- Localized itching or redness, usually resolves after 2‑4 weeks of consistent use.
- Unwanted facial hair growth if the solution drips onto the forehead.
- Rare systemic effects such as low blood pressure, especially if applied in excess.
Finasteride’s concerns revolve around sexual dysfunction (decreased libido, erectile issues) and, in a tiny fraction of cases, mood changes. Women of child‑bearing age should avoid finasteride entirely due to teratogenic risk.
Cosmetic products like Nioxin are essentially risk‑free, but they also lack the robust clinical data to claim true regrowth. Surgical transplants carry infection risk, scarring, and the need for postoperative care, but the results are usually permanent when performed correctly.
Putting It All Together
If you’re just starting to notice thinning around the crown, Lonitab Minoxidil comparison suggests that trying Lonitab alone could give you a measurable improvement within three to six months. Should you hit a plateau, add a DHT‑targeting oral medication or switch to a higher‑concentration foam. For women, a 2% minoxidil formulation (available as Rogaine) may be gentler on the scalp while still delivering results.
When budget isn’t a primary concern and you have advanced balding, a hair transplant delivers the most lasting outcome, but remember it won’t prevent future loss elsewhere. Meanwhile, Nioxin can serve as a supportive daily routine that keeps the scalp healthy and may enhance the effectiveness of medical treatments.
Ultimately, the right choice hinges on the severity of your loss, tolerance for medication, and how much you’re willing to spend. Start with a clear assessment, consult a healthcare professional, and monitor progress carefully. Hair regrowth rarely happens overnight, but with the right plan you can see noticeable improvement within a year.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I use Lonitab and finasteride together?
Yes, many dermatologists prescribe both. Minoxidil (Lonitab) works on the scalp to boost blood flow, while finasteride lowers DHT levels systemically. Using them together can address two major pathways of hair loss, but you should get a doctor’s approval to monitor side effects.
How long does it take to see results with Lonitab?
Most users notice the first signs of thicker strands after 12‑16 weeks of twice‑daily application. Full results typically appear around the six‑month mark, provided you continue consistent use.
Is Lonitab safe for women?
Lonitab is formulated with 5% minoxidil, which is higher than the FDA‑approved 2% concentration for women. Some women tolerate it well, but many experience excess facial hair. Women usually start with a 2% product like Rogaine to gauge sensitivity.
What’s the biggest downside of hair transplant surgery?
The cost and recovery time are the main drawbacks. A single session can run over $10,000, and you’ll need a few weeks of limited activity while the grafts heal. There’s also a small risk of scarring or graft failure if not performed by an experienced surgeon.
Do Nioxin products actually regrow hair?
Nioxin helps improve scalp health and can reduce breakage, making existing hair look fuller. However, it does not contain an FDA‑approved active ingredient that directly stimulates new hair growth, so results are modest compared with minoxidil or finasteride.




June Wx
October 13, 2025 AT 16:25Lonitab sounds pricey but who cares, just buy it.
kristina b
October 19, 2025 AT 04:25The comparative analysis presented in the article offers a comprehensive overview of the pharmacodynamics of minoxidil versus the hormonal modulation achieved by finasteride. It is noteworthy that the systemic absorption of topical minoxidil, while historically considered negligible, has been quantified in recent dermatological studies to range between 0.5% and 1% of the applied dose. This pharmacokinetic nuance underscores the importance of patient education regarding potential off‑target effects, especially in individuals with cardiovascular comorbidities. Furthermore, the discussion of the proprietary solvent system employed by Lonitab raises intriguing questions about the marginal gains in follicular bioavailability that may be attributed to enhanced trans‑epidermal delivery. While the article correctly identifies the cost differential between Lonitab and generic Rogaine, it could benefit from a deeper examination of the long‑term cost‑effectiveness when considering treatment adherence rates. In addition, the table's omission of a comparative metric for patient‑reported satisfaction scores represents a missed opportunity to capture the subjective dimension of therapeutic success. The ethical consideration of prescribing finasteride to women of child‑bearing potential is aptly highlighted, yet the narrative would be strengthened by referencing the latest consensus guidelines from the American Academy of Dermatology. A critical appraisal of Nioxin's role as an adjunctive scalp‑care regimen should also acknowledge the paucity of randomized controlled trials supporting its claimed benefits. The surgical option of hair transplantation is accurately portrayed as a permanent solution; however, the article should caution readers about the necessity of ongoing medical therapy to preserve donor‑site density. It is commendable that the author emphasizes a combination therapy approach, as the synergistic effect of minoxidil and finasteride has been documented in multiple meta‑analyses. Nevertheless, the potential for drug‑drug interactions, particularly with topical corticosteroids used for scalp inflammation, warrants explicit mention. The recommendation to consult a dermatologist before initiating any regimen reflects best practice, yet the piece could incorporate a decision‑tree algorithm to aid patients in navigating the complex therapeutic landscape. Moreover, the psychological impact of hair loss, often underappreciated, deserves a dedicated paragraph discussing coping strategies and the role of support groups. The article’s concluding summary successfully synthesizes the key take‑aways, but a brief outlook on emerging therapies such as platelet‑rich plasma and JAK inhibitors would provide a forward‑looking perspective. In sum, the guide offers a valuable resource for individuals at various stages of alopecia, provided they remain vigilant about side‑effect monitoring and maintain realistic expectations regarding regrowth timelines.
Ida Sakina
October 24, 2025 AT 16:25One must acknowledge that the remedies discussed each possess distinct mechanistic pathways. The minoxidil solutions operate through vasodilation whilst finasteride modulates hormonal synthesis. Ethical considerations arise when prescribing hormonal agents to vulnerable populations. Though the data presented are compelling the writer omits the socioeconomic impact on patient adherence. Ultimately the prudent clinician weighs efficacy against potential systemic sequelae.
Amreesh Tyagi
October 30, 2025 AT 03:25Everyone’s raving about minoxidil but the truth is it’s just a placebo that works for a handful of people the side effects outweigh any minor gain.
Brianna Valido
November 4, 2025 AT 15:25Hey folks! 🎉 If you’re feeling nervous about trying Lonitab just remember that consistency is key and you’ll see those tiny hairs start to look fuller 💪✨ Keep the faith and stay patient, you’ve got this! 🌟
Caitlin Downing
November 10, 2025 AT 03:25i totally get u bria! its sooo easy 2 forget 2 let it dry fully n most peeps get scalp rash cause they sloppily applie it
Robert Jaskowiak
November 15, 2025 AT 15:25Oh great, another miracle bottle that promises a lawn on your head. Because what the world really needed was more overpriced foam.
Julia Gonchar
November 21, 2025 AT 03:25Actually, the FDA approval process for minoxidil products is quite rigorous. The clinical trials required a minimum of 12 months of double‑blind data before any over‑the‑counter label could be granted.
Annie Crumbaugh
November 26, 2025 AT 15:25Looks like a solid overview, nothing too flashy.
Vic Harry
December 2, 2025 AT 03:25Anyone who says a $5,000 transplant is "worth it" clearly never had to work a real job. We need American solutions not foreign luxuries.
Julius Adebowale
December 7, 2025 AT 15:25Look the data shows a 60% failure rate in low‑income groups due to poor follow‑up that pharma ignores. They push the pricey stuff and hide the dropout stats.
KISHORE KANKIPATI
December 13, 2025 AT 03:25What a kaleidoscope of options! From the humble minoxidil potion to the flamboyant surgical choreography, each path paints a different hue on the canvas of confidence. It’s marvelous how science can turn a bald spot into a story of resilience, and I love the way the article stitches together cost, chemistry, and courage into one vibrant tapestry.
Jefferson Vine
December 18, 2025 AT 15:25Did you know that the big pharma lobby secretly funds most of the research that promotes minoxidil? The “independent” studies are just a front for a massive cover‑up designed to keep us buying overpriced creams while they hoard the real cure.