Understanding Calcitonin and Its Role in Bone Health
Calcitonin is a hormone produced by the thyroid gland, and it plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy bones. In this section, we will discuss the basics of calcitonin, its functions, and how it contributes to overall bone health. Understanding this hormone's role is essential for preventing and managing osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weak and fragile bones.
Calcitonin is released in response to high levels of calcium in the blood, and its primary function is to regulate calcium levels. It does this by inhibiting the activity of osteoclasts, cells responsible for breaking down bone tissue and releasing calcium into the bloodstream. By suppressing osteoclast activity, calcitonin helps to preserve bone mass and maintain calcium balance in the body.
The Connection Between Calcitonin and Osteoporosis
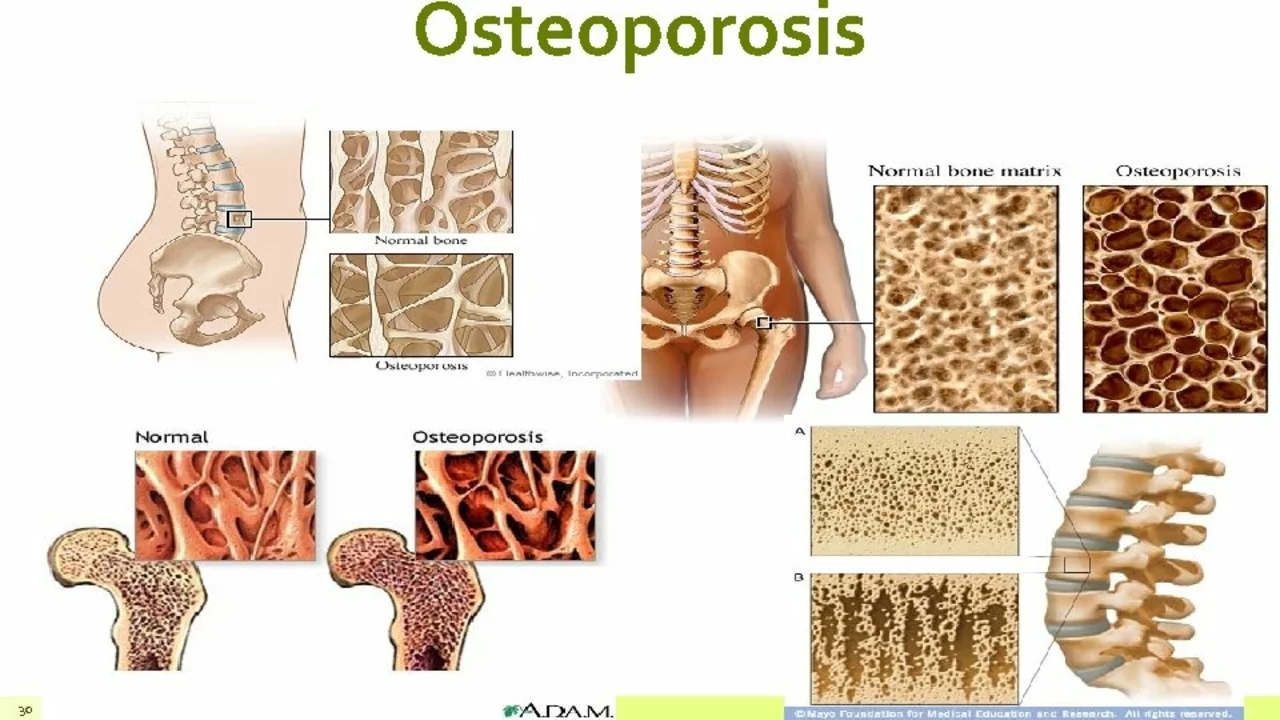
Osteoporosis is a disease that affects millions of people worldwide, and it is characterized by a decrease in bone mass and density, leading to an increased risk of fractures. One of the main factors contributing to the development of osteoporosis is an imbalance between bone formation and bone resorption, the process by which old bone is broken down and replaced by new bone tissue.
As mentioned earlier, calcitonin plays a significant role in regulating bone resorption by inhibiting osteoclast activity. Therefore, having sufficient levels of calcitonin in the body can help prevent excessive bone loss and maintain bone density, ultimately reducing the risk of developing osteoporosis.
Calcitonin as a Treatment for Osteoporosis
Given its beneficial effects on bone health, calcitonin has been used as a treatment for osteoporosis for several decades. Calcitonin is available in various forms, such as injections and nasal sprays, and it is typically prescribed for patients who cannot tolerate other osteoporosis medications or who have contraindications to other treatments.
Studies have shown that calcitonin therapy can help reduce bone pain, increase bone density, and decrease the risk of fractures in individuals with osteoporosis. However, it is essential to note that calcitonin is not considered a first-line treatment for osteoporosis, and it is usually prescribed in combination with other medications and lifestyle interventions.
Monitoring Calcitonin Levels for Optimal Bone Health
Regular monitoring of calcitonin levels can help detect potential bone health issues and prevent the development of osteoporosis. A simple blood test can measure calcitonin levels, and your healthcare provider may recommend this test if you have a family history of osteoporosis, have experienced fractures, or have other risk factors for the disease.
Keeping an eye on your calcitonin levels and discussing any concerns with your healthcare provider can help you take the necessary steps to maintain strong and healthy bones throughout your life.
Calcitonin and Menopause: A Crucial Relationship
Women are at a higher risk of developing osteoporosis, particularly after menopause, as estrogen levels decline. Estrogen is essential for maintaining bone density, and a decrease in this hormone can lead to accelerated bone loss. Interestingly, calcitonin levels also tend to decrease during menopause, further contributing to the risk of osteoporosis.
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is sometimes prescribed to help alleviate menopausal symptoms and protect bone health. HRT can help maintain calcitonin levels, thus supporting bone density and reducing the risk of fractures.
Calcitonin and Nutrition: A Balanced Diet for Bone Health
Maintaining a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients is crucial for bone health and can also help support healthy calcitonin levels. Consuming adequate amounts of calcium and vitamin D is particularly important, as these nutrients play a significant role in bone formation and function. Foods such as dairy products, leafy greens, and fatty fish are excellent sources of these nutrients.
In addition to a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, particularly weight-bearing and resistance exercises, can help strengthen bones and support overall bone health. Consult with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized nutrition and exercise plan that meets your specific needs and promotes optimal bone health.
Conclusion: The Importance of Calcitonin for Bone Health and Osteoporosis Prevention
In conclusion, calcitonin is a vital hormone that plays a significant role in maintaining bone health and preventing osteoporosis. By understanding its functions and the factors that influence calcitonin levels, you can take proactive steps to protect your bones and reduce your risk of developing osteoporosis.
Remember to consult with your healthcare provider before making any significant changes to your diet, exercise routine, or medication regimen, and always prioritize a well-rounded approach to maintaining strong and healthy bones throughout your life.




Kirk Elifson
June 12, 2023 AT 21:21Nolan Kiser
June 13, 2023 AT 04:49Prema Amrita
June 13, 2023 AT 06:03Robert Burruss
June 14, 2023 AT 02:51Alex Rose
June 14, 2023 AT 04:53Patrick Hogan
June 14, 2023 AT 12:25prajesh kumar
June 14, 2023 AT 20:11Arpit Sinojia
June 15, 2023 AT 03:53Kshitiz Dhakal
June 15, 2023 AT 15:54kris tanev
June 16, 2023 AT 14:23Mer Amour
June 17, 2023 AT 02:07